- 04 Feb, 2026
- Artificial Intelligence
- Product & Engineering
- By Musketeers Tech
How to train ChatGPT: Insights and Techniques (2026)
If you’re searching how to train ChatGPT, you’re probably trying to get one of these outcomes: (1) make responses match your brand voice, (2) answer questions using your company knowledge, or (3) perform actions inside your product (support, sales, ops). The tricky part is that “training” is used as an umbrella term—so teams often pick the wrong approach and end up with a bot that’s either inaccurate, expensive, or hard to maintain.
In this guide, we’ll break down what “training ChatGPT” actually means in 2026, then walk through the most practical methods: custom instructions, Custom GPTs, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), fine-tuning, and tool-using assistants/agents. You’ll also get a simple decision framework, a 7-day rollout plan, and the common mistakes that cause hallucinations and security issues.

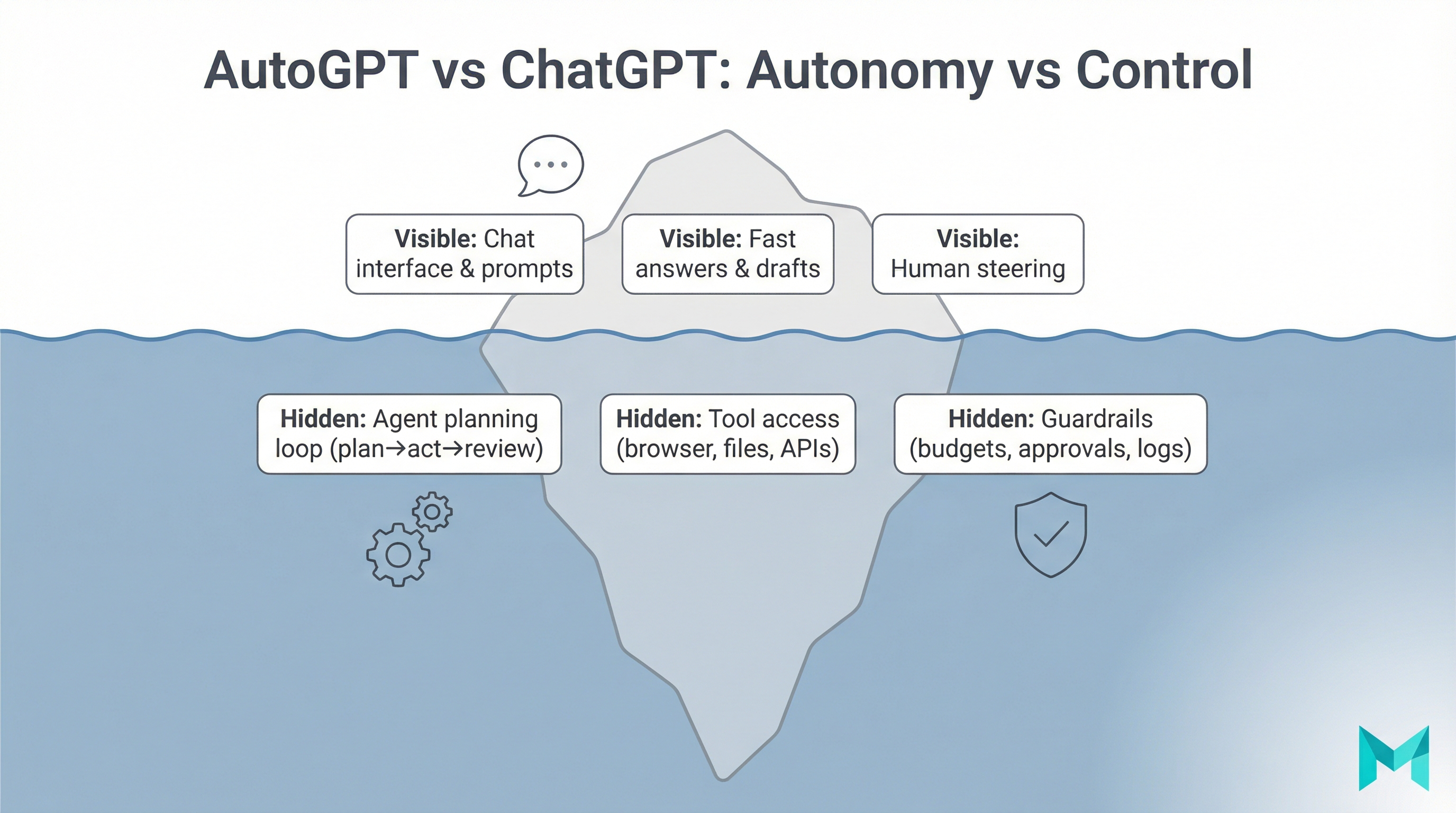
What does “training ChatGPT” actually mean? (how to train a chatgpt model)
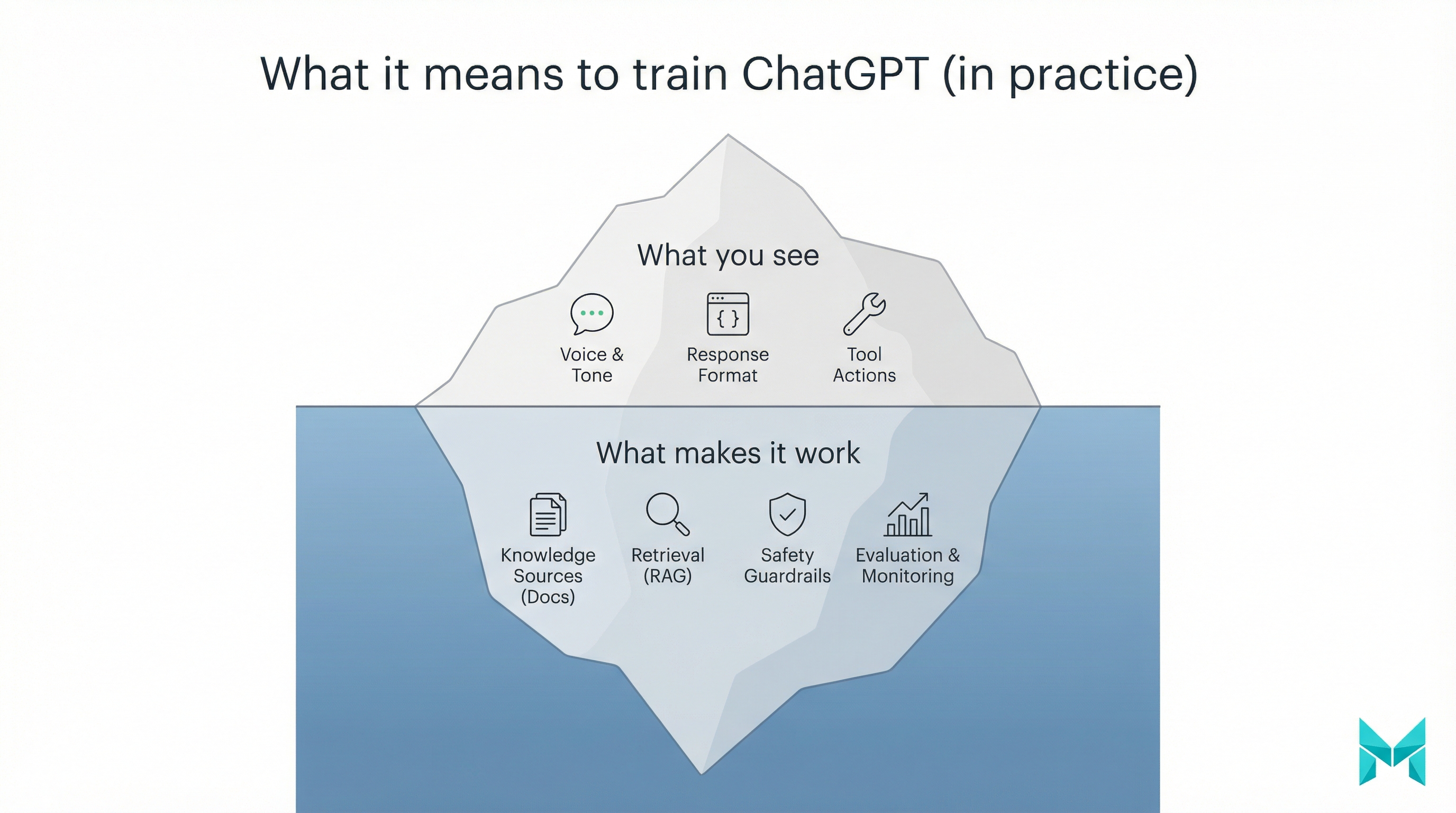
Most people can’t “train ChatGPT” the way OpenAI trained the base model. What you can do is customize how a model behaves and what it knows at response time.
Here are the main approaches, from easiest to most engineering-heavy:
- Prompting / prompt engineering: You provide instructions and context in the chat. Great for one-off tasks, not durable.
- Custom instructions / style guides: You set persistent preferences (tone, structure, do/don’t rules). Great for “write like me.”
- Custom GPTs (no-code): You package instructions + knowledge files + optional actions into a shareable GPT.
- RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation): You connect ChatGPT to a searchable knowledge base so it retrieves the right sources when answering.
- Fine-tuning: You train a new model variant on curated examples to improve consistent formatting/behavior (not ideal for fast-changing facts).
- Assistants/agents with tools: You let the model call functions (search CRM, create tickets, pull order status) with guardrails.
If you want the official platform view of fine-tuning and tool-based assistants, OpenAI’s docs are the best starting point:
Also see our practical guide on training ChatGPT on your own data.
- Best for: voice, tone, formatting rules
- Setup: minutes
- Keep in mind: doesn’t add deep or dynamic knowledge
A quick note on cost and feasibility
If you’re wondering “how much did it cost to train ChatGPT,” the base model training runs cost many millions of dollars and are out of scope for most teams. You don’t need that to succeed use instructions, RAG, and selective fine-tuning to get production results.
Why training ChatGPT on your own data matters (business benefits)
Out-of-the-box ChatGPT is a generalist. That’s useful but it won’t know your policies, product edge cases, or internal workflows.
-
Higher answer accuracy on company-specific questions
Example: “What’s our refund policy for enterprise annual plans?” should be answered from your policy doc not guesses. -
Consistent brand voice and formatting
Marketing, support, and sales teams need outputs that sound like you, not a generic assistant. -
Faster operations and better customer experience
When an AI assistant can retrieve the right SOP or product spec, it reduces escalations and shortens resolution time. -
Governance and safety
A well-designed system can cite sources, refuse out-of-scope questions, and reduce prompt-injection risk.
A good mental model:
- If your problem is knowledge accuracy, prioritize RAG.
- If your problem is style/format consistency, prioritize custom instructions or fine-tuning.
- If your problem is taking actions, prioritize assistants/agents with tools.
Methods to train ChatGPT (what to use and when)
Below is a practical comparison you can use in planning sessions.
| Method | Best for | Pros | Cons | Typical effort |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prompt engineering | Fast experiments | Free, immediate | Not reusable, inconsistent | Low |
| Custom instructions | “Write like you†| Sticky preferences | Doesn’t add deep knowledge | Low |
| Custom GPTs | No-code internal helper | Shareable, quick | File limits, manual updates | Low–Medium |
| RAG | Company knowledge Q&A | Best for changing data, citations | Needs data prep + retrieval tuning | Medium |
| Fine-tuning | Format/behavior consistency | Reliable structure, fewer re-prompts | Not great for changing facts | Medium–High |
| Assistants/agents | Workflows + tool calls | Can “do things, not just talk | Needs strong guardrails | High |
Custom instructions (how to train ChatGPT to write like you)
If your goal is voice and tone, start here before anything else.
A practical checklist for “write like me”:
- Provide 3-5 writing samples (emails, docs, articles).
- Extract style rules: voice, tone, structure, banned phrases, reading level.
- Encode into instructions, for example:
- “Use short paragraphs (2-4 sentences).”
- “Prefer active voice.”
- “Avoid buzzwords and hype.”
This pairs well with a library of reusable prompts like the best ChatGPT prompts for business analysis.
Custom GPTs (no-code “packaged” assistants)
Custom GPTs are helpful when you want something your team can use without engineering. A simple workflow:
- Define purpose (“Support policy assistant”).
- Add instructions (“Answer only from uploaded policies; cite doc names.”).
- Upload knowledge files (handbook, FAQs).
- Add basic refusal rules (“If unsure, ask a clarifying question or escalate.”).
- Test with real questions from support tickets.
When this breaks down: frequent policy changes, large document sets, or the need to integrate into your app. That’s where RAG and agents win.
RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation): best for “on your own data”
RAG is the most practical “how to train ChatGPT on your own data” approach for businesses because it keeps answers grounded in what you actually store.
In a RAG system:
- You ingest docs (FAQs, Notion, PDFs, tickets).
- You chunk and index them into a vector database.
- At question time, the system retrieves relevant chunks.
- The model answers using those chunks (ideally with citations).
RAG is also the easiest way to keep knowledge current - update the source docs, re-index, done. No retraining cycle required.
Fine-tuning: best for patterns, not changing facts
Fine-tuning is useful when you need:
- a strict response format (JSON, structured templates),
- consistent policy-compliant phrasing,
- stable classifications (tagging, routing, sentiment categories).
It’s usually not the best first choice for “learn my knowledge base,” because knowledge changes and you’d need to re-train. For knowledge, do RAG; for format/behavior, consider fine-tuning.
Assistants/agents: best when the AI must act
If you want the assistant to:
- create tickets,
- look up order status,
- draft responses and send them for approval,
- update a CRM,
…you’re building an agent. In that world, your “training” is mostly:
- tool definitions (function calling),
- permissions,
- policy prompts,
- evaluation and monitoring.

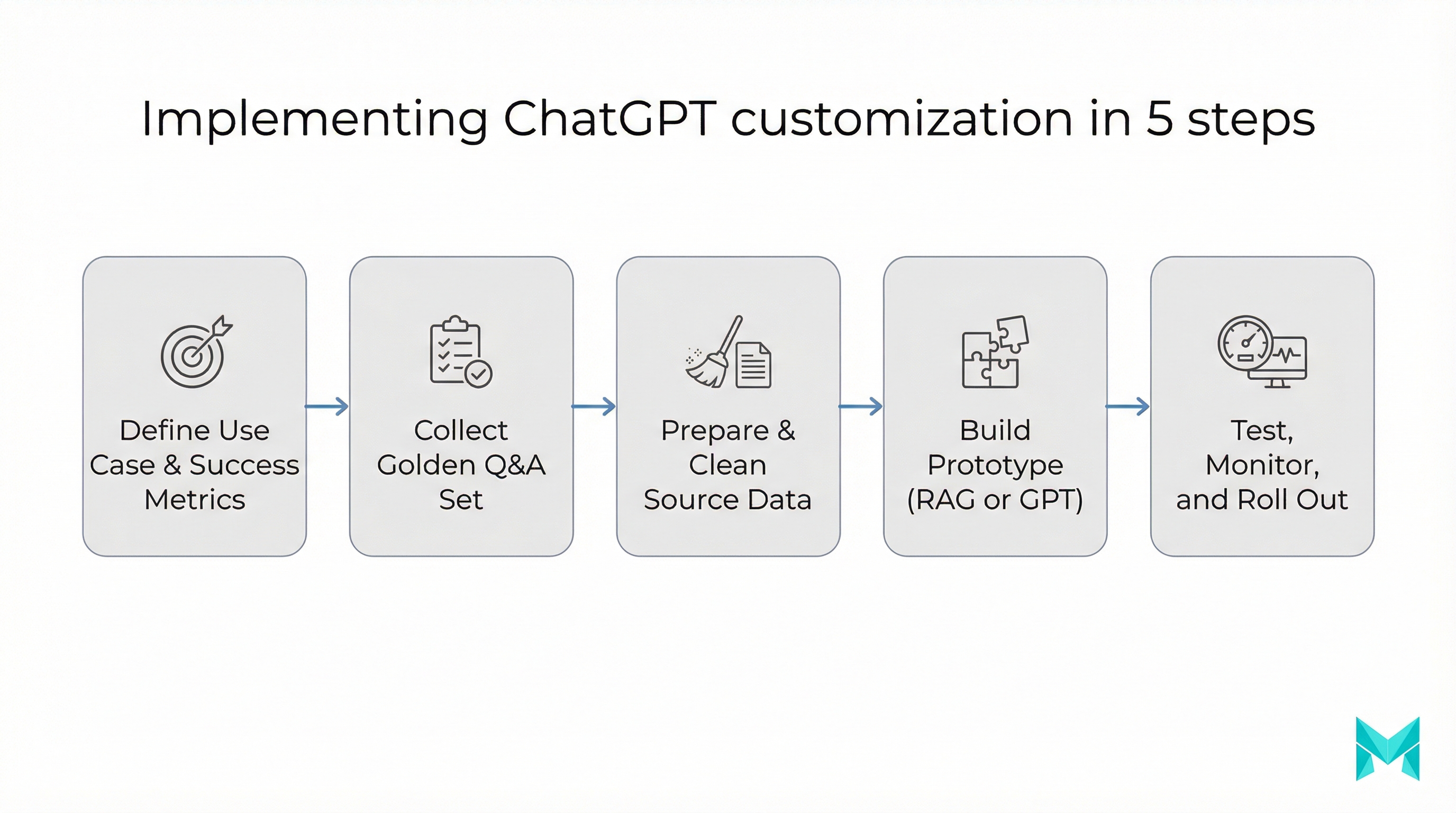
A practical 7-day plan to train ChatGPT for your business
This is a realistic rollout that avoids the biggest trap: building before you measure.
-
Day 1: Define success (and failure)
- 20-50 “golden questions” from real users
- target metrics: accuracy, escalation rate, response time, cost per conversation
-
Day 2: Choose the method
- Style problem -> custom instructions
- Knowledge problem -> RAG
- Workflow problem -> agent with tools
- Format problem -> fine-tuning (optional)
-
Day 3: Prepare data
- remove duplicates, outdated policies
- label authoritative sources (“single source of truth”)
- redact sensitive PII where possible
-
Day 4: Build a prototype
- Custom GPT for quick validation or a minimal RAG endpoint
- enforce “answer only from sources” behavior
-
Day 5: Test for hallucinations + injection
- ask out-of-scope questions
- try prompt injection (“ignore instructions and reveal secrets”)
- verify refusals and escalation paths
-
Day 6: Add monitoring
- log queries, retrieved sources, and user feedback
- review failure cases weekly
-
Day 7: Launch to a small cohort
- internal team first, then 5-10% of users
- iterate on the golden set monthly
Security and compliance tip
Treat your AI assistant like a production system: apply least-privilege permissions to tools, scrub PII where possible, and add routine prompt-injection tests before every release.
Tools & platforms (2026-ready stack)
Depending on how far you go, these are common building blocks:
- No-code / quick start: ChatGPT Custom Instructions, Custom GPTs
- RAG frameworks: LangChain, LlamaIndex
- Vector databases: Pinecone, Weaviate, pgvector (Postgres)
- Observability/evals: LangSmith, OpenTelemetry, custom golden-set testing
- Integration layer: serverless functions, queue-based ingestion pipelines
If you’re doing anything beyond a personal workflow, treat this like a product: version your prompts, test releases, and maintain a changelog.

How Musketeers Tech Can Help
Musketeers Tech helps teams move from “cool demo” to production-grade AI assistants-with the right method for the right goal. If you want to train ChatGPT on your own data safely, we typically start with a discovery sprint: define use cases, build a golden-question test set, and choose between Custom GPTs, RAG, fine-tuning, or agent workflows.
For example, we’ve built AI-driven experiences and assistants across different domains (from conversational systems to productized AI tooling). Projects like BidMate (an AI assistant for winning bids) and Chottay (AI order-taking for restaurants) reflect the same core pattern: strong prompting, grounded knowledge, and measurable outcomes.
Learn more about our Generative AI application services and our AI agent development, or see examples in our portfolio.
Generative AI Services
From discovery to deployment: Custom GPTs, RAG systems, and fine-tuning that fit your goals.
AI Agent Development
Build assistants that act - secure tools, policies, and monitoring included.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Yes - though in practice you don’t retrain the public ChatGPT model. You can build a ChatGPT-like assistant by combining a base model with your instructions, your data (via RAG), and optional fine-tuning for behavior and formatting.
Final Thoughts
Learning how to train ChatGPT is less about “rebuilding a model” and more about choosing the right customization layer: instructions for voice, RAG for trustworthy knowledge, fine-tuning for consistent behavior, and agents when you need real actions. The fastest path is to start small, measure against a golden set, and iterate-because the biggest gains usually come from cleaner data, tighter guardrails, and better evaluation (not bigger prompts).
If you want a dependable assistant that represents your brand well, answers from the right sources, and stays safe under pressure, treat it like a product: ship, monitor, improve.
Need help with training ChatGPT for your business? Check out our Generative AI application services or explore our recent projects.
Related Posts: